Description Sum of Left Leaves
Table of Contents
Given the root of a binary tree, return the sum of all left leaves.
A leaf is a node with no children. A left leaf is a leaf that is the left child of another node.
Example 1
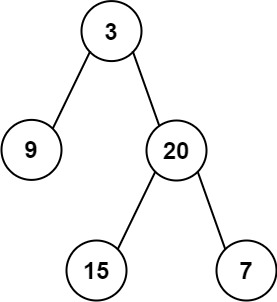
|
1 2 3 |
<strong>Input:</strong> root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] <strong>Output:</strong> 24 <strong>Explanation:</strong> There are two left leaves in the binary tree, with values 9 and 15 respectively. |
Example 2
|
1 2 |
<strong>Input:</strong> root = [1] <strong>Output:</strong> 0 |
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solution
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 |
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) { if(root==null){ return 0; } if(root.left==null && root.right==null){ return 0; } int[] sum = new int[1]; //use a flag to identify if the node is left or right dfs(root, false, sum); return sum[0]; } //preorder traversal private void dfs(TreeNode node, boolean isLeft, int[] sum){ if(node==null){ return; } if(node.left==null && node.right==null){ if(isLeft){ sum[0]+=node.val; } } dfs(node.left, true, sum); dfs(node.right, false, sum); } } |
Time Complexity
O(n): where is the number of nodes in a binary tree
Space Complexity
O(1)